National Income is a unit that includes 4 chapters in itself. This article includes all these 4 chapters. Here are the national income class 12 notes.
Topics Discussed
Meaning of Circular Flow
It refers to the cycle of generation of income in the production process, its distribution among the factors of production & finally its circulation from the households to firms in the form of consumption expenditure on goods & services produced by them.
Phases of Circular Flow of Income
There are 3 different phases in the circular flow of income:
1) Generation/Production Phase
This phase involves the production of goods and services with the help of factors services like land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurs.
2) Distribution/Income Phase
This phase involves the flow of factor’s income namely rent, wages, interest, and profit from firms to households.
3) Disposition/Expenditure Phase
In this phase, income received by factors of production is spent on goods and services produced by the firm.
Difference between Stock and Flow
| Basis | Stock | Flow |
| Meaning | Stock variable refers to the variable which is measured at a particular point in time. | Flow variables refer to that variable which is measured over a period of time. |
| Time Dimension | It does not have a time dimension. | It has a time dimension as its magnitude can be measured over a period of time. |
| Concept | It is a static concept. | It is a dynamic concept. |
| Examples | Population of India on 01.01.2024, Money Supply, etc. | Number of births during 2023, National Income. |
Difference between Real and Money Flow
| Basis | Real Flow | Money Flow |
| Meaning | It is the flow of goods & services between firms and households. | It is the flow of money between firms and households. |
| Kinds of exchange | It involves the exchange of goods & services. | It involves the exchange of money. |
| Difficulty in exchange | There may be difficulties with barter systems in the exchange of goods & services. | There is no such difficulty in the case of money flow. |
| Alternative name | It is also known as Physical Flow. | It is also known as Nominal Flow. |
Circular Flow of Income in Simple Economy
A simple economy assumes the existence of only two sectors i.e. household and firm sectors.
Households are the owners of the factor of production & consumers of goods and services.
Firms produce goods and services & sell them to households. It is the simplest form of a closed economy, in which there is no government sector & foreign trade.
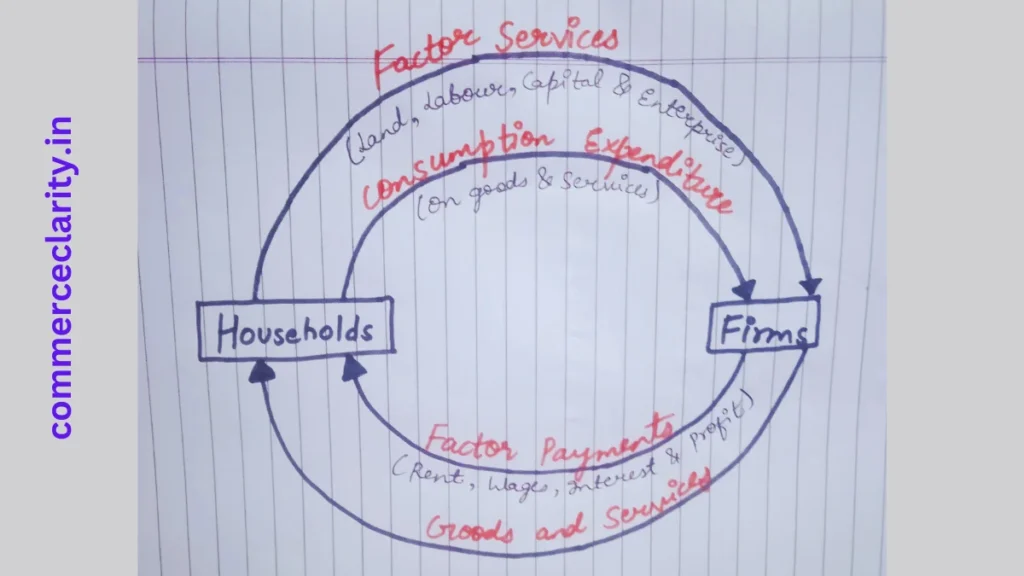
The outer loop of the diagram shows the real flow i.e. flow of factor services from households to firms & and the corresponding flow of goods & services from firms to households.
The inner loop shows the money flow i.e. flow of factor payments from firms to households & the corresponding flow of consumption expenditure from households to firms.
Domestic Territory
Domestic territory refers to the political frontiers of a country. It also includes embassies, Fishing vessels, oil and natural gas rigs operated by residents in international waters, ships, and aircraft owned and operated by normal residents between two or more countries.
Note: Domestic territory does not include embassies, consulates, and military establishments of a foreign country.
International organizations like UNO, WHO, etc are also not included.
Normal Residents
It refers to an individual or an institution that ordinarily resides in the country and whose center of economic interest also lies in that country.
Citizenship
It is a legal concept and to become a citizen of a country, you have to either be born in that country or have to comply with some legal provisions.
Residentship
It is an economic concept and to become a resident of a country, you have to ordinarily reside in that country for a period more than 1 year and your economic interest should also lie in that country.
Difference between Factor and Transfer Income
| Basis | Factor Income | Transfer Income |
| Meaning | It refers to income received by factors of production for rendering factor services. | It refers to income received without rendering any productive service. |
| Nature | It is included in both national as well as domestic income. | It is neither included in national nor in domestic income. |
| Concept | It is an earning concept. | It is a receipt concept. |
| Examples | Rent, wages, Retirement Pension, etc. | Old age pension, scholarship, etc. |
Difference between Final and Intermediate Goods
| Basis | Final Goods | Intermediate Goods |
| Meaning | It refers to the goods which are either used for consumption or for investment. | It refers to those goods which are either used for resale or for further production in the same year. |
| Nature | Included in both national and domestic income. | Neither included in national nor domestic income. |
| Value addition | No value has to be added to the final goods. | Some value has to be added to the intermediate goods. |
| Production boundary | These goods have crossed the production boundary. | These goods are still within the production boundary. |
| Example | Maggie purchased by households. | Maggie purchased by a shopkeeper. |
Note: Chalks, dusters, etc purchased by a school are intermediate products as these are purchased by schools as an input to facilitate educational services.
Difference between Consumption and Capital Goods
| Basis | Consumption Goods | Capital Goods |
| Satisfaction of Human Wants | These goods satisfy human wants directly. | These goods satisfy human wants indirectly. |
| Production Capacity | These goods do not promote production capacity. | They help in raising production capacity. |
| Expected Life | Except for durable goods, these goods have limited life expectancy. | Capital Goods generally have more than 1 year life expectancy. |
Difference between Depreciation and Capital Loss
| Basis | Depreciation | Capital Loss |
| Meaning | It refers to a fall in the value of fixed assets due to normal wear and tear, passage of time, etc. | It refers to the loss in value of fixed assets due to unforeseen obsolescence, accidents, etc. |
| Provision for Loss | Provision is made for depreciation. | No provision is made for capital loss. |
| Production Process | It does not hamper the production process. | It hampers the production process. |
National Income
It is the income of a nation and can be considered the most comprehensive measure of the performance of an economy.
National Income = NNP at fc
Domestic Income = NDP at fc
Methods of Calculating National Income
There are three methods of calculating national income:
1) Income Method
2) Expenditure Method
3) Value Added Method
Income Method
In the Income Method, we add all the income to get national income.
NDP(at fc) = Profit + Rent & Royalty +Interest + Mixed Income + Compensation of Employees
You can learn this formula by a mnemonic named PRIME where;
P- Profit
R- Rent and Royalty
I- Interest
M- Mixed Income
E- Compensation of Employees
Operating Surplus = Profit + Rent & Royalty + Interest
Profit = Undistributed Profits + Corporate Tax + Dividend
Compensation of Employees = Comp. in cash + Comp. in-kind + Social Security schemes by the employer
Expenditure Method
In the Expenditure Method, all the expenditure on the purchase of goods and services produced by firms is added to find the national income.
GDP(at mp) = Private final consumption expenditure + Govt. final consumption expenditure + Gross domestic capital formation + Net exports
Net exports = Exports – Imports
Gross domestic capital formation = Gross domestic fixed capital formation + Change in Stock
Change in stock = Closing Stock – Opening Stock
Indian economy on the eve of independence notes
Value Added Method
In the value-added method, the value added by each sector in the production process is added up to find the national income.
GVA(at mp) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
Note: GVA(at mp) = GDP(at mp)
Value of Output = Sales + Change in Stock
Change in Stock = Closing Stock – Opening Stock
Difference between Nominal and Real Income
| Basis | Nominal Income | Real Income |
| Meaning | It refers to the monetary value of final goods and services measured at current-year prices. | It refers to the monetary value of final goods and services measured at prices of the base year. |
| Causes of Change | It is affected by changes in both price and quantity. | It is affected by change in the quantity only. |
| Comparison | Not suitable for comparison. | Suitable for comparison. |
| Calculation | Current Price (P1) * Current Quantity (Q1) | Base Year Price(P0) * Current Quantity(Q1) |
| Alternative Name | It is also known as national income at the current price. | It is also known as national income at a constant price. |
GDP and Welfare

Higher GDP doesn’t mean greater welfare of people but generally, people associate higher GDP with more welfare of people.
Here are some of the limitations of GDP:
- Distribution of GDP: It may happen that with the rise in GDP, the gap between rich and poor also rises.
- Change in Price: If the increase in GDP is due to a rise in prices then it is not a reliable index for economic welfare.
- Non-Monetary Exchanges: Many activities like services of a housewife, and kitchen gardening are not included in GDP.
- Externalities: It refers to the benefits or harms of an activity caused by a firm or an individual for which they are not paid or penalized.
- Rate of Population Growth: GDP does not consider the change in the population of a country.
These are the national income class 12 notes. If you have doubt, you can either join my telegram channel or comment below to resolve your doubts.
[…] National Income Class 12 Notes All Formulas […]