
Foreign exchange refers to all the currencies other than the domestic currency of a given country e.g., India’s domestic currency is the Indian Rupee & all other currencies like the US Dollar, British Pound, etc. are foreign exchanges.
Here are the foreign exchange rate class 12 notes.
Topics Discussed
Foreign Exchange Rate
It refers to the rate at which one currency exchanges for the other. It represents the price of one currency in terms of another currency.
For example – If one $ can be exchanged for Rs. 80 then the value of Rs. 1 will be:
Rs. 1 = 1/80$
Rs. 1 = 0.0125$
Difference between Currency Appreciation & Currency Depreciation
| Basis | Currency Depreciation | Currency Appreciation |
| Meaning | It refers to a decrease in the value of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. | It refers to an increase in the value of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency. |
| Effect on exports/imports | It makes domestic goods cheaper in foreign countries as more such goods can now be purchased with the same amount of foreign currency. So, it leads to an increase in exports. | It makes foreign goods cheaper in domestic countries as more such goods can now be purchased with the same amount of domestic currency. So, it leads to an increase in imports. |
| Example | A change from $1=Rs.80 to $1=Rs.85 represents that the Indian rupee is depreciating. | A change from $1=Rs.80 to $1=Rs.75 represents that the Indian rupee is appreciating. |
Reasons for Rise in Demand for Foreign Currency
- Import of goods & services: Foreign exchange is demanded to make the payment for import of goods & services.
- Tourism: Foreign exchange is needed to meet expenditures incurred in foreign tours.
- Purchase of assets in foreign countries: It is demanded to make payments for the purchase of assets like land shares, bonds, etc. in foreign countries.
- Unilateral transfers to abroad: Foreign exchange is required for making unilateral transfers like sending gifts to other countries.
- Speculation: Demand for foreign exchange arises when people want to gain from the appreciation of the currency.
Reasons for Rise in Supply of Foreign Exchange
- Exchange of goods & services: Supply of foreign exchange comes through exports of goods & services.
- Foreign investments: The amount foreigners invest in home countries increases the supply of foreign exchange.
- Uni-lateral transfers from abroad: Supply of foreign exchange increases in the form of gifts & other remittances from abroad.
- Speculation: Supply of foreign exchange comes from those who want to speculate on the value of foreign exchange.
Types of Foreign Exchange Rate

There are 3 types of exchange rate system:
a) Fixed Exchange Rate System
b) Flexible/Floating Exchange Rate System
c) Managed Floating Rate System
Fixed Exchange Rate System
It refers to a system in which the exchange rate for a currency is fixed by the government. The basic purpose of adopting this system is to ensure stability in foreign trade & capital movements.
To achieve stability, the government undertakes to buy foreign currencies. When the exchange rate becomes weaker and sells foreign currency the exchange rate gets stronger.
Under this system, each country keeps the value of its currency in terms of some external standard. This external standard can be gold, silver, other precious metals another country’s currency, or some internationally agreed unit of account.
When the value of a domestic currency is tied to the value of another currency, it is termed as pegging and when the value of currencies is fixed in terms of gold or silver, etc. it is known as parity value.
Flexible Exchange Rate System
It refers to a system in which the exchange rate is determined by forces of demand & supply of different currencies in the foreign exchange market.
Under this system, the value of currency is allowed to fluctuate freely according to changes in the demand & supply of different currencies.
There is no government intervention under this system. It is also known as the floating exchange rate.
Managed Floating Rate System
It refers to a system in which the foreign exchange rate is determined by market forces & central bank influences the exchange rate through intervention in the foreign exchange market. It is a hybrid of the fixed exchange rate and the flexible exchange rate system.
In this system, central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market to restrict the fluctuations in the exchange rate within certain limits.
The aim is to keep the exchange rate close to the desired target values. It is also known as dirty floating.
Difference between De-valuation & Depreciation
| Basis | De-valuation | Depreciation |
| Meaning | It refers to the reduction in the price of domestic currency in terms of all the foreign currencies under the fixed exchange rate regime. | It refers to a fall in the market price of domestic currency in terms of a foreign currency under the flexible exchange rate regime. |
| Occurrence | It takes place due to the government. | It takes place due to market forces of demand and supply. |
| Exchange Rate | It takes place under the fixed exchange rate system. | It takes place under the flexible exchange rate system. |
Difference between Fixed Exchange Rate and Flexible Exchange Rate
| Basis | Fixed Exchange Rate | Flexible Exchange Rate |
| Meaning | It refers to a system in which the exchange rate for a currency is fixed by the government. | It refers to a system in which the exchange rate is determined by the forces of demand and supply. |
| Determination of Exchange Rate | It is officially fixed in terms of gold or any other currency by the government. | It is determined by market forces of demand & supply of foreign exchange. |
| Government Control | There is complete government control as only the government has the power to change it. | There is no government intervention & it fluctuates freely according to market conditions. |
| Stability in Exchange Rate | The exchange rate generally remains stable & only a small variation is possible. | The exchange rate keeps on changing. |
Government Budget Class 12 Notes
Foreign Exchange Market
Foreign Exchange Market is a market in which foreign currencies are bought and sold. The buyers & sellers include individuals, firms, commercial banks, central banks & foreign exchange brokers.
Functions of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market performs 3 main functions:
- Transfer Function: It transfers purchasing power between the countries involved in the transaction. This function is performed through credit instruments like bills of foreign exchange, bank drafts, and telephonic transfers.
- Credit Function: It provides credit for foreign trade. Bills of exchange with a maturity period of 3 months are generally used for international payments.
Credit is required for this period to enable the importer to take possession of goods, sell them & obtain money to pay off the bill. - Hedging Function: When exporter & importer agree to sell & buy goods on some future date at the current prices & exchange rate. It is called hedging.
The purpose of hedging is to avoid losses that might be caused due to exchange rate variations in the future.
Kinds of Foreign Exchange Market
There are two kinds of foreign exchange markets:
1) Spot Market
2) Forward Market
Spot Market
It refers to the market in which the receipts & payments are made immediately. Generally, a time of 2 business days is permitted to settle the transaction.
The spot market is daily & deals only in spot transactions & not in future transactions.
The rate of exchange that prevails in the spot market is known as the spot exchange rate or current rate of exchange.
Forward Market
It refers to the market in which the sale & purchase of foreign currency is settled on a specified future date at a rate agreed upon today.
The forward exchange rate is used in forward transactions. Forward exchange rate becomes useful for both the parties involved in transactions & forward contract is made for 2 reasons:
- To minimize the risk of loss due to adverse changes in the exchange rate (through hedging).
- To make profits (through speculation).
Determination of Exchange Rate
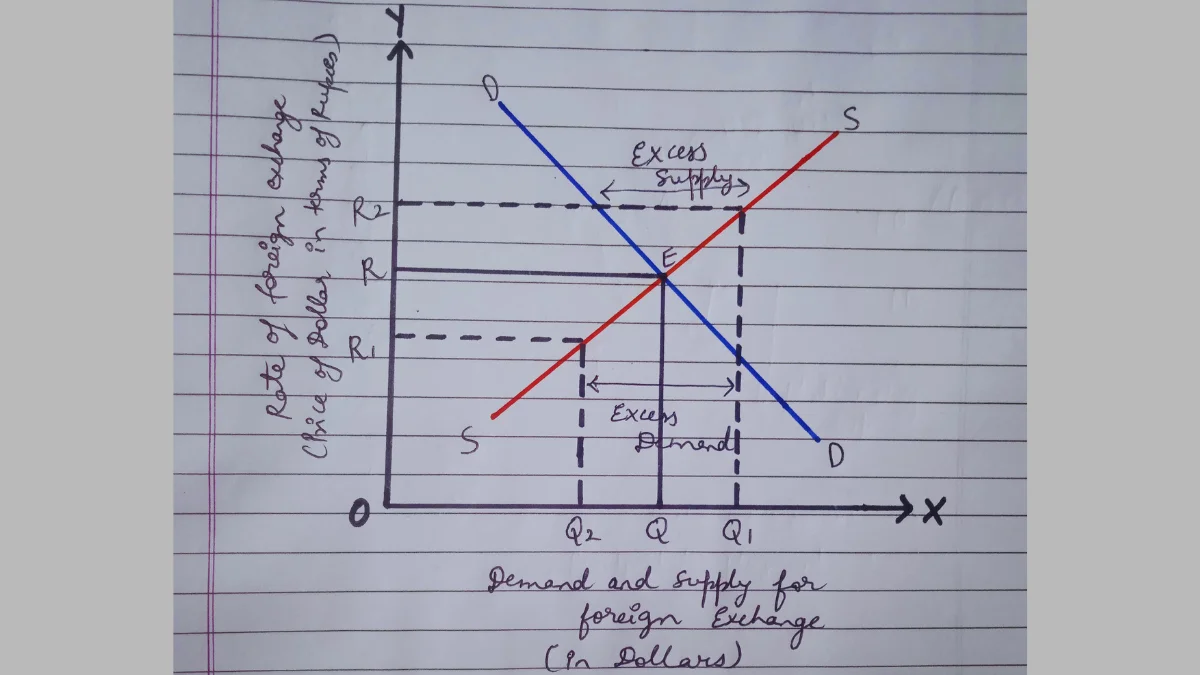
- The equilibrium exchange rate is determined at a level where the demand for foreign exchange is equal to the supply of foreign exchange.
- In the diagram, demand & supply of foreign exchange is measured on the x-axis & the rate of foreign exchange on the y-axis. DD is the downward-sloping demand curve of foreign exchange & SS is the upward-sloping supply curve of foreign exchange.
- Both the curves intersect each other at point E. The equilibrium exchange rate is determined at OR & equilibrium in quantity is determined at OQ.
[…] Foreign Exchange Rate Class 12 Notes […]